Introduction. What is Grasshopper?
Parametric building structures.
The parametric structures design is a tool that allows us to explore solutions that beforehand we do not know. This tool simply establishes input parameters and rules between them. The development of parametric design computer tools, such as Grasshopper and Dynamo, has allowed to create a visual programming more accessible to users with little experience in other areas of programming. It allows to create complex geometries from the association of geometric components and parameters.
Visual programming.
Visual programming consists of a visual editor and a 3d modeling environment. In the virtual editor, the algorithm that performs a certain task is developed. In the 3d modeling environment, the resulting geometry is obtained.
In the visual editor you can find different objects: parameters and components. The main ones are the parameters, which store the data or the starting geometry. The components are the elements that perform actions on the parameters. Both elements are linked with wired connections. In this way, it is very easy to follow the algorithm flow.
What is Grasshopper.
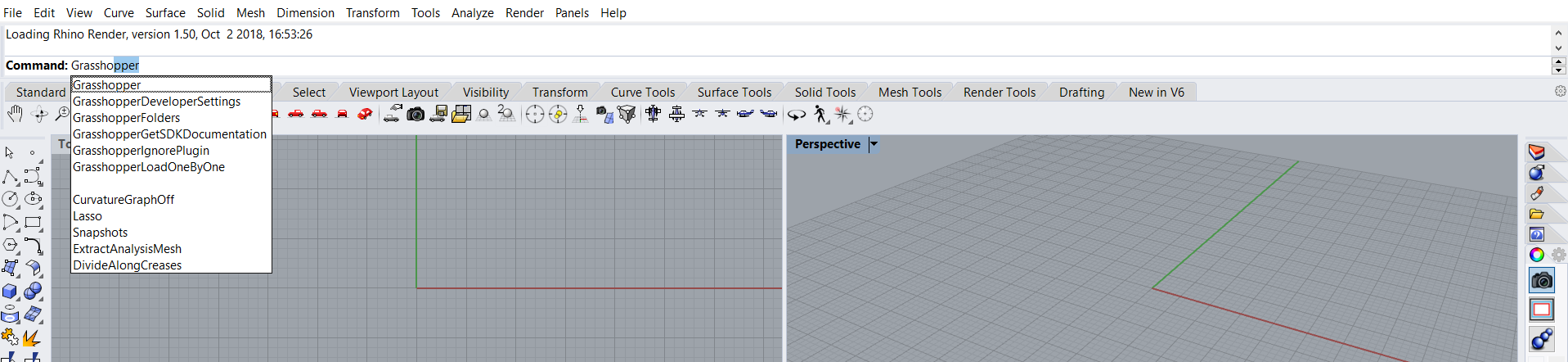
Grasshopper is a plug-in that is installed in Rhinoceros. But you just must call it. To do this, type Grasshopper on the command line, and press Enter key. As you type, it shows us the available commands and options.
This software is design-oriented, allowing the modelling of simple or complex shapes through interconnected parameters and components. It is ideal for parametric design.
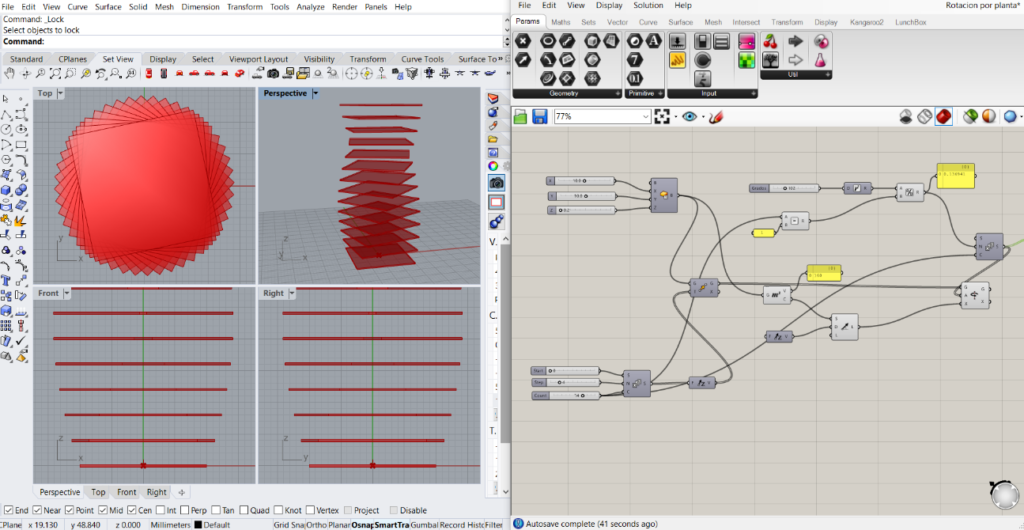
Its interface is the following:
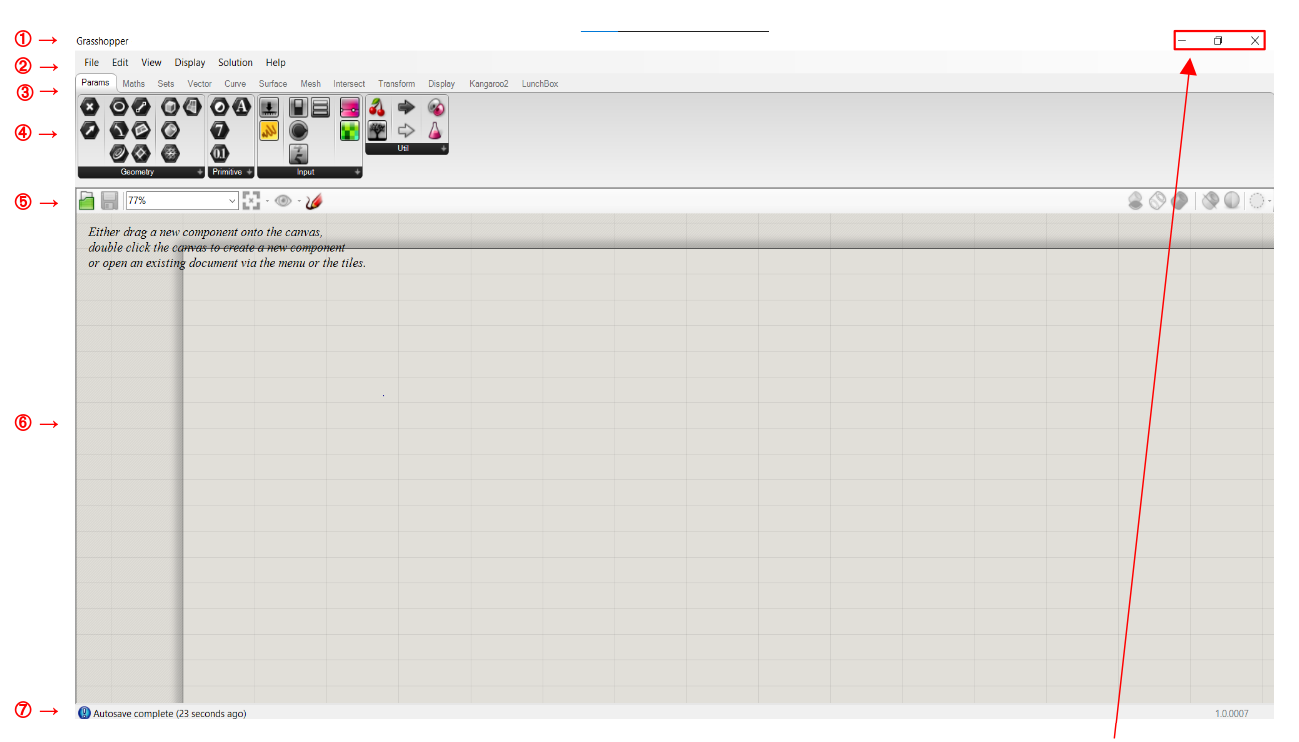
Where
① →Title bar: display the software name and the file name you are working with. There are also the minimise and close window options.
② → Main Menu Bar: it has six drop-down menus. In this section, you can quickly switch between various uploaded files.
③ → Options ribbon: it gives you access to all the commands available in the software. They are classified them by themes.
④ → Icon bar: it displays and classifies all the components available in Grasshopper.
⑤ → Canvas Toolbar: it provides quick access to some commonly used functions and others related to the visualization of objects.
⑥ → Workspace or canvas: it is the area where parameters and components are inserted and linked to create the project.
⑦ → Status bar: it provides information on the main events that have occurred, and it shows the version of the plug-in.
