BIM Course
Introduction
This document proposes the curriculum of a specialization course entitled Building Information Modelling in Architecture, Engineering and Construction Industry. This course is designed to be taught in tertiary vocational training.
The course has three versions with the following credits each:
- Course A: BIM in AEC Industry. 6 Credits
- Course A+: BIM in AEC Industry. 8 Credits
- Course A+B: BIM in AEC Industry. 12 Credits
Each credit corresponds to 10 lecture hours.
People who pass of these specialization courses may exercise their activity in public or private companies of the architecture, engineering, and construction sector. That is companies that develop projects under the BIM methodology, whose activities have a clear tendency to the digitalization of the processes of development of information models of projects and assets.
The most relevant occupations and jobs are the following:
a) BIM modeler.
b) Coordinator of BIM models.
Structure
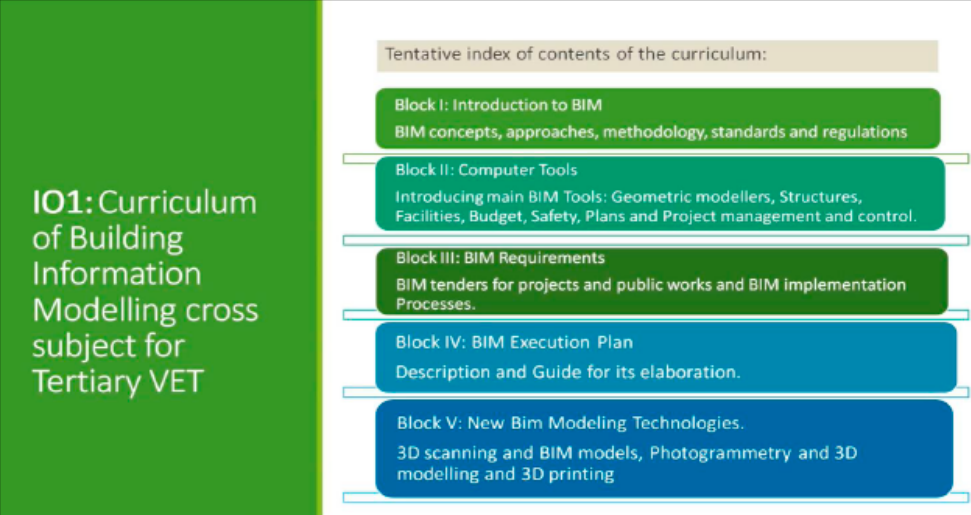
The index of the contents of the curriculum of the course

The index of the contents of the curriculum of the course
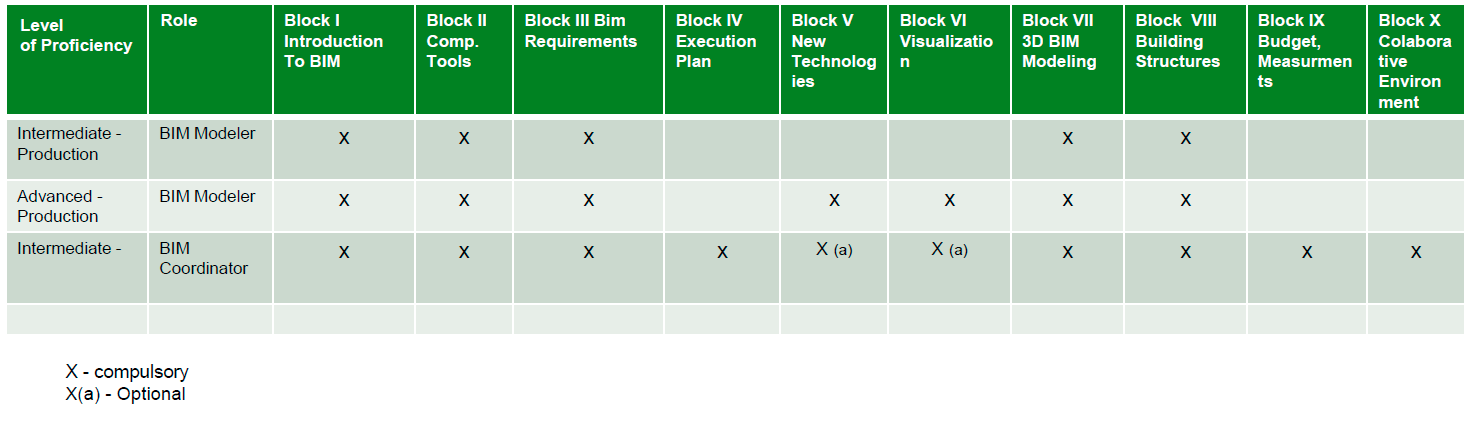
Definition of the learning blocks for each level of proficiency and role.
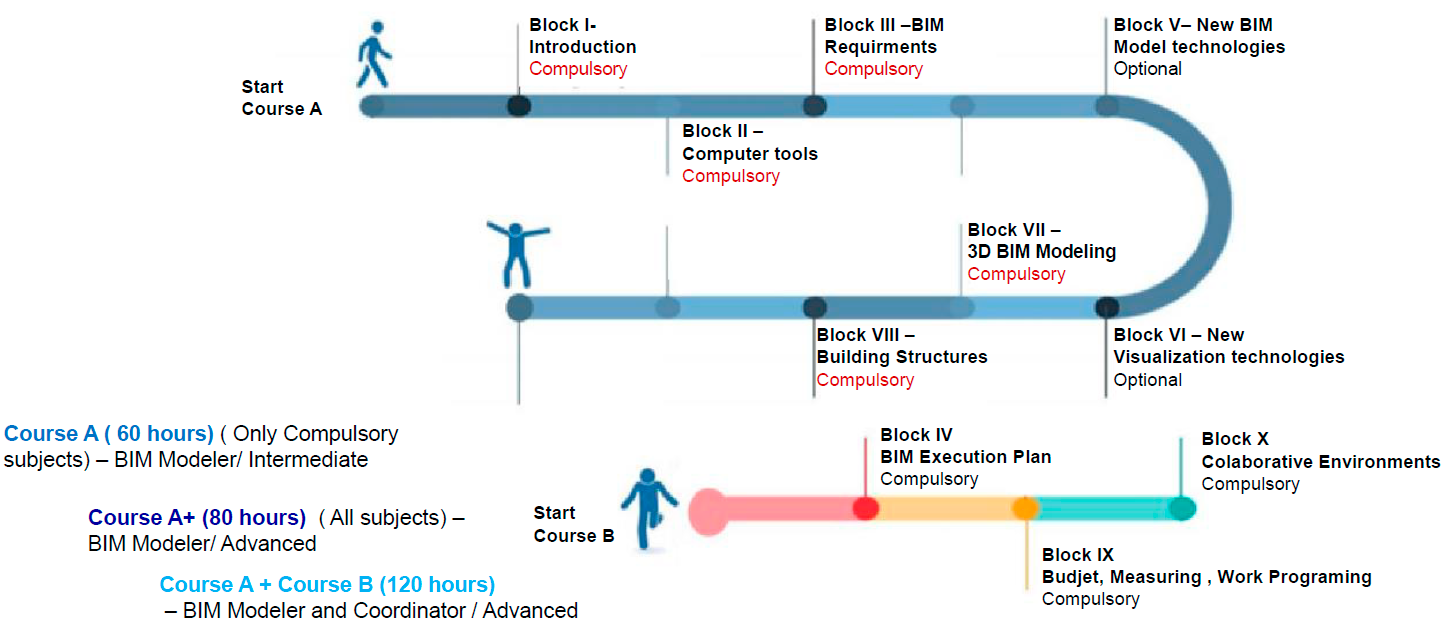
Definition of course lecture hours for each level of proficiency and role.
Goals
The general goals of this specialization course are the following:
a) To analyze project documentation under the BIM methodology, its dimensions, level of detail and definition, workflows, BIM uses, collaboration processes to know the scope of work.
b) To establish the workflows among the different project specialties to use the necessary computer tools according to the client’s requirements.
c) To model BIM objects of different specialties by introducing the necessary parameters to store the necessary graphic and non-graphic information.
d) Using the necessary computer tools to obtain the necessary information and data from the virtual model.
e) To model buildings and infrastructures of different disciplines and specialties to have the project information models.
f) To carry out collision detection processes in the models to communicate and resolve incidents improving the efficiency of the project.
g) To design and configure custom view templates and drawings of the virtual model for the documentation generation automation.
h) To link BIM models to work planning diagrams to supervise and control the different execution phases.
j) To develop creativity and the innovation spirit to respond to the challenges that arise in the processes and in the work organization and personal life.
Competences
GC: The general competence of this specialization course consists of developing and modeling the graphic and non-graphic information of Architecture, Engineering and Construction projects under the BIM methodology in its different dimensions, as well as collaborating in the projects processes, respecting the client’s requirements (EIR, Employer’s Information Requirements) and the prescriptions established in the BIM Execution Plan (BEP, Building Execution Plan).
Specific competences:
SC1: To prepare the project technical documentation under the BIM methodology, its dimensions, level of detail and definition, workflows, BIM uses, collaboration processes, among others.
SC2: To determine and represent the work processes among the different project specialties according to the established requirements.
SC3: To develop BIM objects of different specialties by introducing the necessary parameters.
SC4: To identify the processes of modeling graphic and non-graphic information to obtain information and data from the virtual model.
SC5: To develop virtual models with graphic and non-graphic information of the different specialties present in the project.
SC6: To report on the results and measures to be adopted after subjecting the federated model to collision detection (crash detection).
SC7: To configure custom view templates and drawings of the model for the automation of documentation generation.
SC8: To supervise and control the model from the association of work planning diagrams.
SC9: To associate price databases to the BIM model enabling the automation of budget generation.
SC10: To obtain three-dimensional models of point clouds and other technologies from the survey of the current state with 3D scanner technology and the treatment of information.
SC11: To apply augmented, mixed and virtual reality techniques to BIM models to display the model.
SC12: To manage and administer the information of the virtual models that may be required in the management processes of asset maintenance and contributing to the needs of circular economy.
BIM Course Tutorials
Go to BIM Course Tutorials
